Photo by
ArtsyBeeKids
on
Pixabay
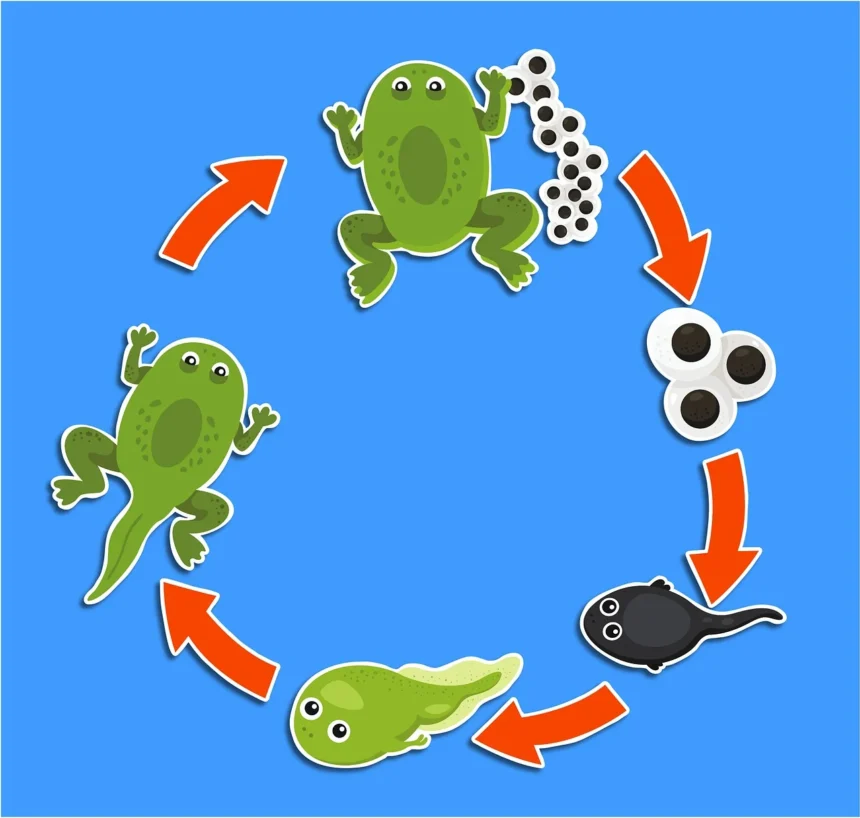
Life cycle, an intriguing concept in biology, outlines the fascinating series of changes undergone by a species as it navigates its existence from the inception of development to the dawn of a similar stage in the following generation. This captivating journey, often displayed as a circular diagram, encapsulates the stages of birth, growth, reproduction, and death, presenting a perpetual cycle of life.
- The Concept of Life Cycles
1.1 Defining Life Cycles
A life cycle is a sequence of biological changes that a species undergoes from the start of a given developmental stage to the beginning of the same stage in the next generation. In the broad context of science, it is generally represented as a circular diagram showcasing each stage pictorially or textually. This diagrammatic representation signifies the endless nature of the cycle, with seeds or offspring being produced as part of the process, thereby perpetuating life.
1.2 Importance of Life Cycles
The study of life cycles is a crucial aspect of understanding the natural world. It not only aids in comprehending various biological processes but also helps in grappling with profound concepts like birth, growth, reproduction, and death. Life cycles unravel the intricate relationship between different species and their environment, providing insights into the principles of survival, adaptation, and evolution.
- Categories of Life Cycles
2.1 Haplontic Life Cycle
In a haplontic life cycle, the organism’s life cycle predominantly occurs in the haploid stage. The diploid phase is limited to a single cell, the zygote. The organism begins with the fission of an individual, grows to maturation, and then splits into new individuals, completing the cycle. This type of life cycle is observed in simple organisms such as bacteria and various protists.
2.2 Diplontic Life Cycle
In the diplontic life cycle, the diploid stage is multicellular, and haploid gametes are formed. The organism commences its journey with the fusion of male and female sex cells (gametes), grows to reproductive maturity, and then produces gametes, initiating the cycle again. This life cycle is characteristic of higher animals.
2.3 Haplodiplontic Life Cycle
A haplodiplontic life cycle, also known as a diplohaplontic life cycle, includes both a diploid generation (the sporophyte) and a haploid generation (the gametophyte). This life cycle is characteristic of most plants, some protists, and fungi.
- Life Cycles Across Diverse Species
3.1 Life Cycle of Plants
In most plants, the life cycle is multigenerational. It begins with the germination of a spore, which grows into a gamete-producing organism (the gametophyte). The gametophyte forms gametes, which, following fertilization, grow into a spore-producing organism (the sporophyte). When the sporophyte reaches reproductive maturity, it produces spores, and the cycle starts again. This multigenerational life cycle is also known as the alternation of generations.
3.2 Life Cycle of Animals
The life cycle of animals encompasses a single generation. The individual animal commences with the fusion of male and female sex cells (gametes), grows to reproductive maturity, and then produces gametes. The cycle starts anew with fertilization.
3.3 Life Cycle of Insects
The life cycle of insects, such as mosquitoes, comprise different stages from egg to adult. The adult female lays eggs which develop into larvae, pupae, and finally adults. Reproduction completes and perpetuates the cycle.
3.4 Parasitic Life Cycle
Parasites, which depend on the exploitation of one or more hosts, often display complex life cycles that involve infecting more than one host species to complete their life cycles. For example, the heartworm, Dirofilaria immitis, has an indirect life cycle, starting with a microfilariae ingested by a female mosquito, developing into the infective larval stage, and then being transmitted to an animal where they mature into adults.
- Life Cycles and Evolution
Life cycles, through their diverse manifestations across species, play a crucial role in the evolutionary processes. Evolutionary processes can change the heritable characteristics in interbreeding populations of organisms from one generation to the next. The study of life cycles contributes to the understanding of these processes, thereby enriching our knowledge about the evolution of different species. - Human Intervention in Life Cycles
Human activities have significantly altered the life cycles of various species. These activities range from fishing and hunting, which often removes large reproductively mature individuals from species populations, to habitat destruction due to deforestation, agricultural activities, and urbanization. Such interventions can lead to the evolution of new traits or alterations in life cycles for the species to survive in changing ecosystems. - Life Cycles in Education
Learning about life cycles is an integral part of the educational curriculum, from early childhood to higher grades. It helps children understand and deal with concepts such as life, death, and birth. Children are introduced to the life cycles of different animals, plants, and insects through real-world examples and hands-on activities, promoting a deep understanding of the relevant scientific concepts.